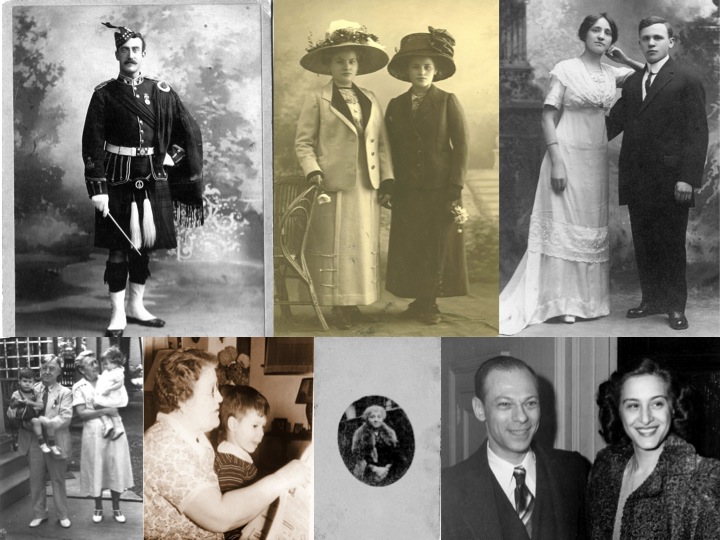
I have dozens of letters and a few postcards written to one of her nieces, dating from the early 1980s and continuing until shortly before her death nearly 20 years later.
"Auntie" wrote of life after retiring from her teaching career, about her travels, about being in touch with relatives, about her health, and more.
I found some really interesting family history tidbits in her letters. Did Dorothy's grandpa Moritz Farkas (1867-1936) play favorites? Dorothy says Moritz's oldest daughter was his favorite--even though another of Moritz's daughters insisted she was always the favorite. And that's just one example.
Put a sleeve on it
Yesterday I finished carefully unfolding and inserting each letter into a clear archival resealable sleeve, sliding the envelope in the back of each sleeve, to keep everything safe for the future. (This was long after I had removed staples, clips, and rubber bands.)
The letters, flat and straight in their sleeves, will be organized chronologically. Some don't have years, just day and month at top of the letter, and a few have no envelopes with postmarks. I'll have to "guess" the year based on what each undated letter says. At some point, I'll scan the letters but for now, I want to smooth them out and keep them safe.
Next step: For easy storage, I like to box things up.
Box things up
My favorite storage method is the archival box. As shown above, I buy boxes with metal corners so they can be stacked 6 high without giving way. Boxes come in a variety of sizes to fit nearly every kind of genealogical item that can lay flat, such as a document or a photo or an album or even a Bible.
I use my trusty label maker to add a descriptive label on the short side and the long side of each box, so I can read the contents no matter which side faces out.
As soon as I finish arranging my aunt's letters, that box will join the rest of the archival boxes of documents and photos in my home office--including the box above, containing letters written home during World War II by service members in my Farkas family tree.
Transcribe for accessibility
I've previously transcribed the WWII letters and sent copies of the letters and transcriptions to my cousins, the children and grandchildren of those service members. Years ago, I transcribed letters written to my mother during the late 1940s, when she met and was courted by my father. Other letters still await transcription.
Meanwhile, the letters are safely stored and will go to designated genealogy heirs when I join my ancestors someday.
--
For more about organizing, curating, and preserving family history for the sake of future generations and future researchers, please take a look at my concise, affordable book, Planning a Future for Your Family's Past, available on Amazon, at the American Ancestors book store/catalog, and at the Newberry Library book store.